When you think about milk fever, does your mind immediately go to the weak, down cows that require IV calcium treatment?
In reality, these clinical hypocalcemia cases are just the tip of the iceberg. They are the visible representation of a much larger underlying problem. This doesn’t only apply to herds with a high incidence of milk fever either.
A recent study on a progressive dairy in Texas digs deeper into the fundamentals of calcium shortages in mature cows after calving. The study addresses whether supplementing cows in their 2nd and greater lactations with one application of two RumiLife CAL24 boluses at calving actually affected fresh cow health, production, and reproductive status.
Here are the myths and truths that this study revealed.
MYTH: You’ll only see a lucrative ROI from CAL24 if you’re currently experiencing fresh cow troubles
It may be easy to assume that an already high-performing farm may not see much of an ROI from CAL24. However, the data uncovered in this recent study suggests that even a well-managed herd can see an ROI of nearly $46.
Here are the initial stats about the herd and more information about the study:
The Herd
- 3500 cows | 40% Jersey, 40% Jersey x Holstein cross, 20% Holstein
- 75 lbs per day of energy corrected milk (ECM) across the herd
- <2% Milk Fever incidence
The Study
- This study took place from October 2020 through November 2021
- A total of 2608 cows in their second or greater lactation were included in the study and divided into two groups
- Test group: Each cow received on administration of two CAL24 boluses shortly after calving
- Control group: Cows did not receive calcium supplementation after calving
The Results
Test group cows treated with one application of two RumiLife CAL24 boluses after calving had fewer cases of retained placenta and milk fever, more milk yield, and fewer days open, which leads to lower costs for semen and synchronization. When you total that up, and then subtract the cost of the boluses and the labor to administer them, this dairy saw nearly a $46 return on investment for every cow treated with CAL24.

TRUTH: CAL24 decreases the incidence of milk fever and other detrimental health events
The study clearly showed a decrease in not only milk fever in the CAL24 test group but also fewer cases of retained placenta and mastitis. This finding is important because the results are from a well-managed dairy with relatively low incidences of these health events already.
Progressive dairies that don’t have a high rate of these health events may think they don’t have much to gain by administering CAL24 to all cows in the 2nd lactation and beyond. However, the findings from this study indicate otherwise. Regardless of a dairy’s current health performance, CAL24 provides room for improvement.

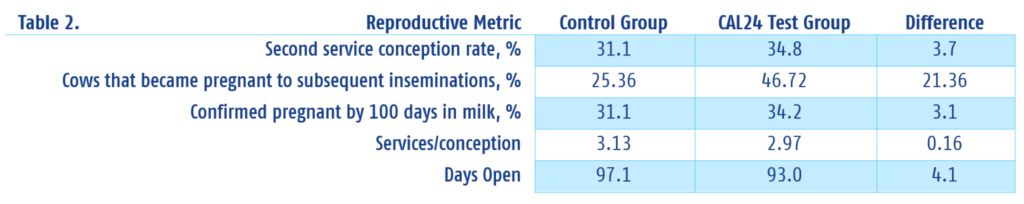
TRUTH: CAL24 increases milk yield
Based on official DHIA test day milk recording, this study compared milk production between the control group and the CAL24 test group. To do that, the scientists measured first test day milk yield, fat corrected milk, and energy corrected milk averages of both groups.
As the table shows, the cows that received CAL24 treatment after calving had higher recorded weights for all milk and component production at their first test and throughout the first 170 days of their lactations.
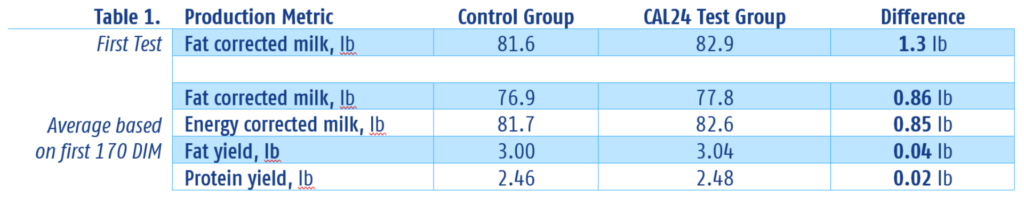
TRUTH: CAL24 improves reproductive performance
This study followed the control group and CAL24 test group cows into their lactations to measure reproductive performance. The herd follows a 60-day voluntary wait period, and the table below compares the repro results between the control group and the CAL24 test group.
First service conception rates were similar between the two study groups. As Table 2 shows, second service conception rates were higher in the CAL24 test group. There were also a higher percentage of cows in the CAL24 test group that became pregnant to subsequent inseminations, which led to the test group having more cows confirmed pregnant by 100 days in milk, less average days open, and requiring fewer services per conception.